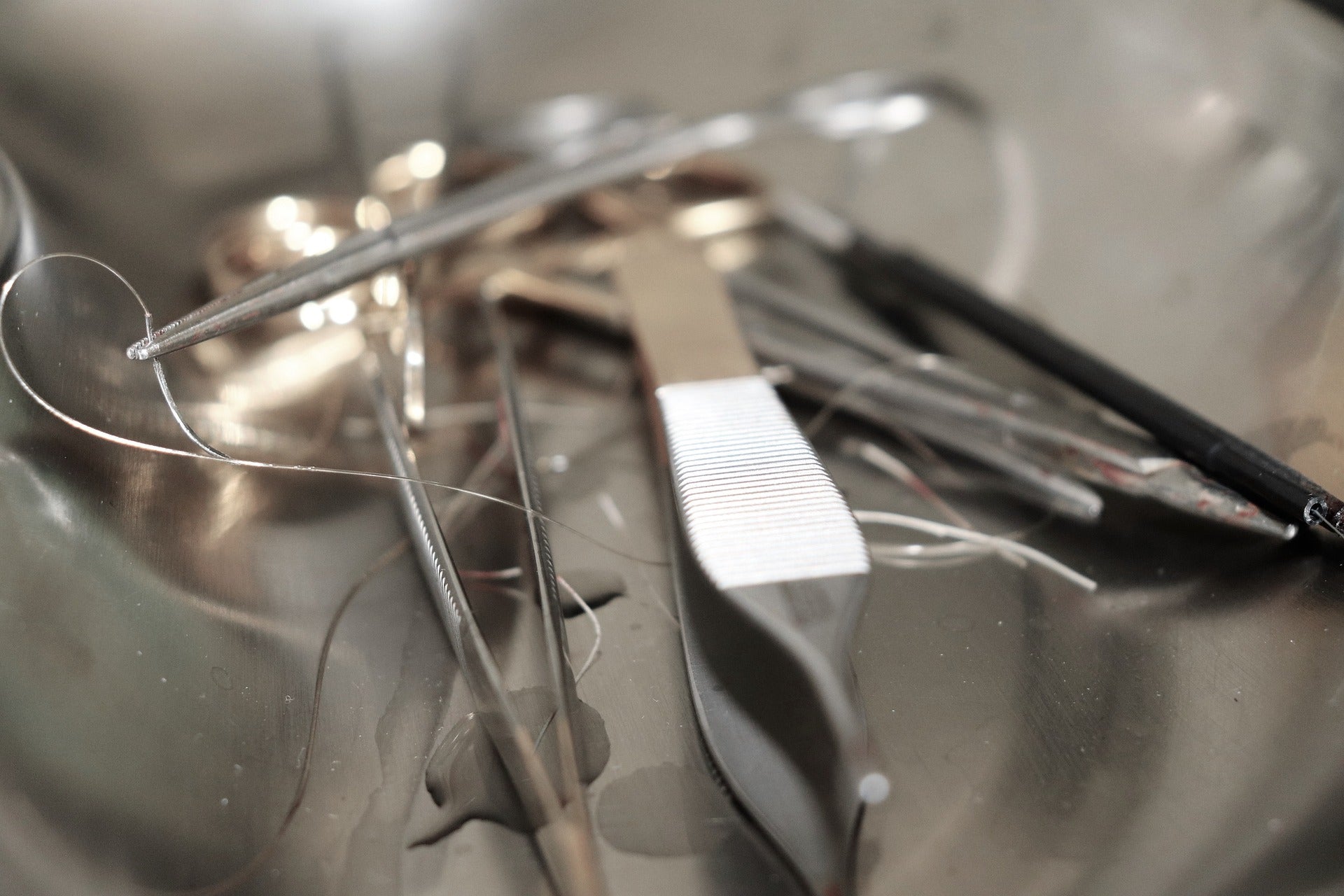
- Cleaning: Instruments should be thoroughly cleaned after each use to remove any blood, tissue, or other debris. This can be done manually or in an ultrasonic cleaner.
- Sterilization: Sterilization is necessary to eliminate any bacteria or other pathogens that may be present on the instruments. Sterilization can be done using steam sterilization (autoclaving), chemical sterilization, or gas sterilization.
- Inspection: Regular inspection of instruments should be performed to ensure they are in good working order and to identify any signs of wear or damage.
- Proper storage: Instruments should be stored in a dry, cool place and protected from damage. If possible, store them in a tray or container designed specifically for that instrument to prevent damage to delicate parts.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as sharpening or oiling, should be performed to keep instruments in optimal working condition.
- Repairs: Instruments that are damaged or not working properly should be repaired or replaced as soon as possible.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining a record of cleaning, sterilization, and maintenance processes can be useful for quality control and to ensure that instruments are being properly maintained over time.
These best practices help to ensure that surgical instruments are in good working order and ready for use in the operating room, reducing the risk of surgical complications and improving patient outcomes.